Echocardiography
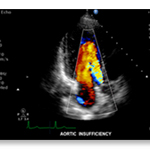
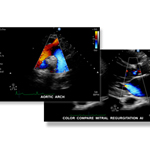
An echocardiogram is an ultrasound exam of the heart and is sometimes referred to as an ECHO, or a cardiac ultrasound. An echocardiogram images two dimensional slices of the heart. Echocardiography can help diagnose cardiovascular disease. It is one of the most widely used diagnostic imaging tests for heart disease. It can provide a vast amount of diagnostic information, including the shape and size of the heart, the pumping capacity of the heart and the location and extent of any damage to the tissues of the heart. An echocardiogram is most useful for assessing any disease to the heart valves.
An echocardiogram can detect abnormalities in of blood flow patterns, such as the reverse flow of blood through partly closed heart valves, which is known as regurgitation. Echocardiography can assess the motion of the heart wall, which can help detect the presence of and assess the severity of CAD or coronary artery disease. It can also help determine whether experienced chest pain is related to heart disease. Echocardiography can also help diagnose hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, which occurs when the walls of the heart thickens in an attempt to compensate for any weakness to the heart muscle. Echocardiography is noninvasive, which means that it doesn't involve breaking the skin and has no known side effects or risks to the patient’s health.
