Venous Duplex Imaging
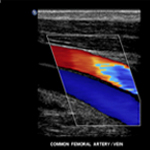
The most common reason for a venous ultrasound exam is to search for blood clots, especially in the veins of the leg. This condition is often referred to as deep vein thrombosis or DVT. These clots may break off and pass into the lungs, where they can cause a dangerous condition called pulmonary embolism. If found in time, there are treatments that can prevent this from happening.
A venous ultrasound study is also performed to:
-
Determine the cause of long-standing leg swelling. In people with a common condition called varicose veins, the valves that keep blood flowing in the right direction may not work well, and venous ultrasound can help the surgeon decide how best to deal with this condition.
-
Aid in the placement of a needle or catheter in a large interior vein. Sonography can help locate the exact site of the vein and avoid complications, such as bleeding or air in the chest cavity.
-
Map out the veins in the leg or arm so that segments may be removed and used to bypass an area of disease. An example is using pieces of vein from the leg to surgically bypass narrowed coronary arteries..
-
Examine a blood vessel graft used for dialysis if it is not working as expected; an area of narrowing in the graft may be responsible.
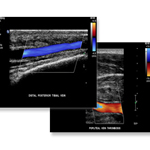
Doppler ultrasound images can help the physician to see and evaluate:
-
blockages to blood flow (such as clots) .
-
venous insufficiency (reflux).
-
narrowing of vessels (which may be caused by plaque).
-
tumors and congenital malformation.
